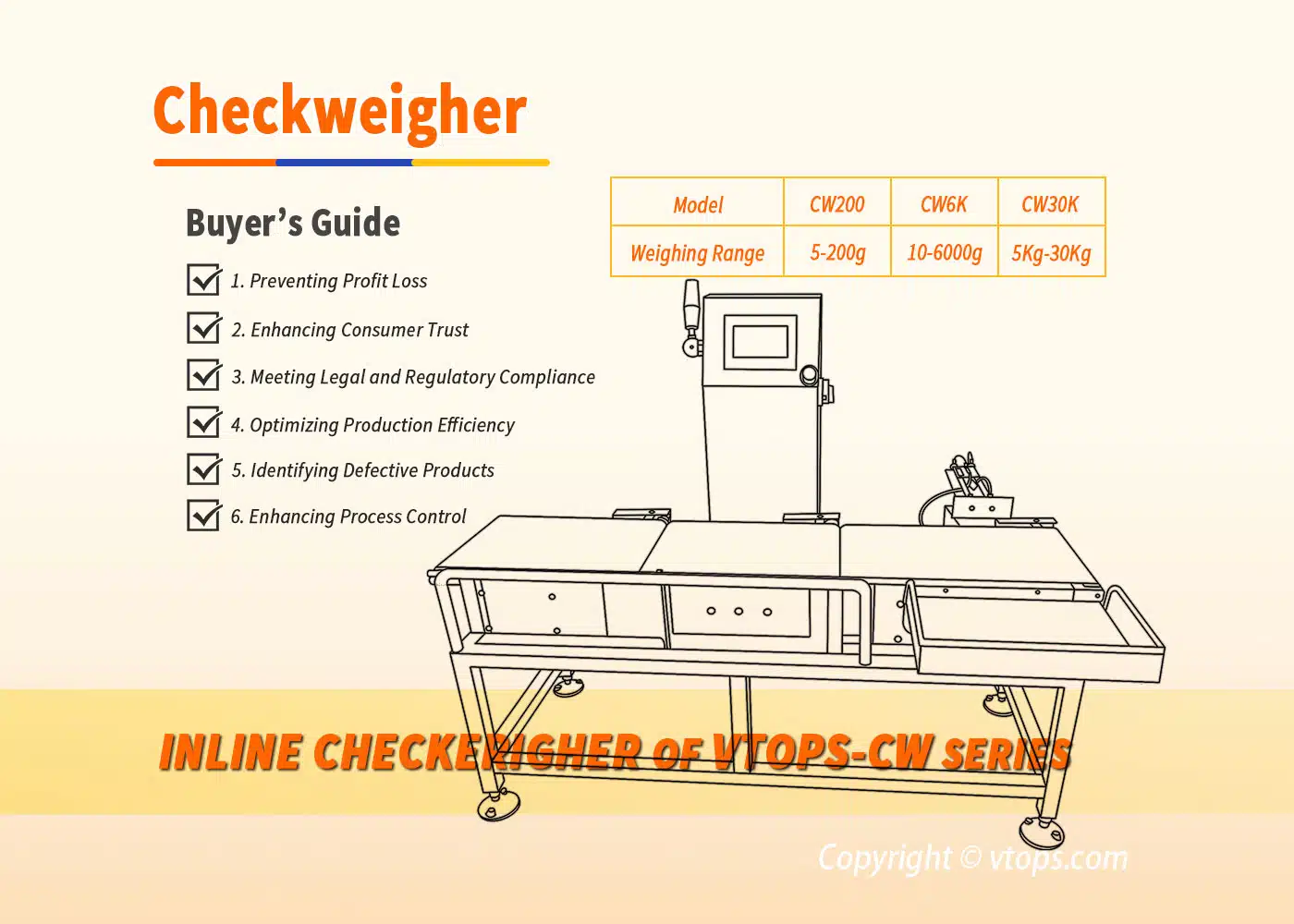
Screw Feeder vs. Vacuum Feeder: Understanding the Key Differences and Best Applications for Bulk Material Conveying
In the domain of bulk material conveying, screw feeders and vacuum feeders are indispensable tools utilized across industries such as packaging, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. While both systems are engineered to transport bulk materials effectively, their operating principles, applications, and advantages differ significantly. Gaining a clear understanding of these distinctions is essential for selecting the most suitable equipment for your specific requirements. Let’s delve into these two technologies in detail.
What is a Screw Feeder?
A screw feeder (also known as a spiral conveyor or auger conveyor) uses a rotating helical screw blade to move materials along a fixed tube or trough. It’s a reliable and widely used solution for conveying powders, granules, and small particulates in a controlled and consistent manner.
Key Features of Screw Feeders
- Mechanism: Rotating screw drives materials forward through a stationary channel.
- Material Suitability: Ideal for bulk materials like flour, grains, or fine powders.
- Capacity: Capable of high-volume material transfer with consistent output.
- Application Range: Commonly used in agriculture, food production, construction, and industrial packaging processes.
What is a Vacuum Feeder?
A vacuum feeder relies on suction created by a vacuum pump to pull materials through an enclosed pipeline. This method is particularly effective for transferring lightweight, fine, or non-sticky materials over longer distances or in applications requiring high levels of cleanliness.
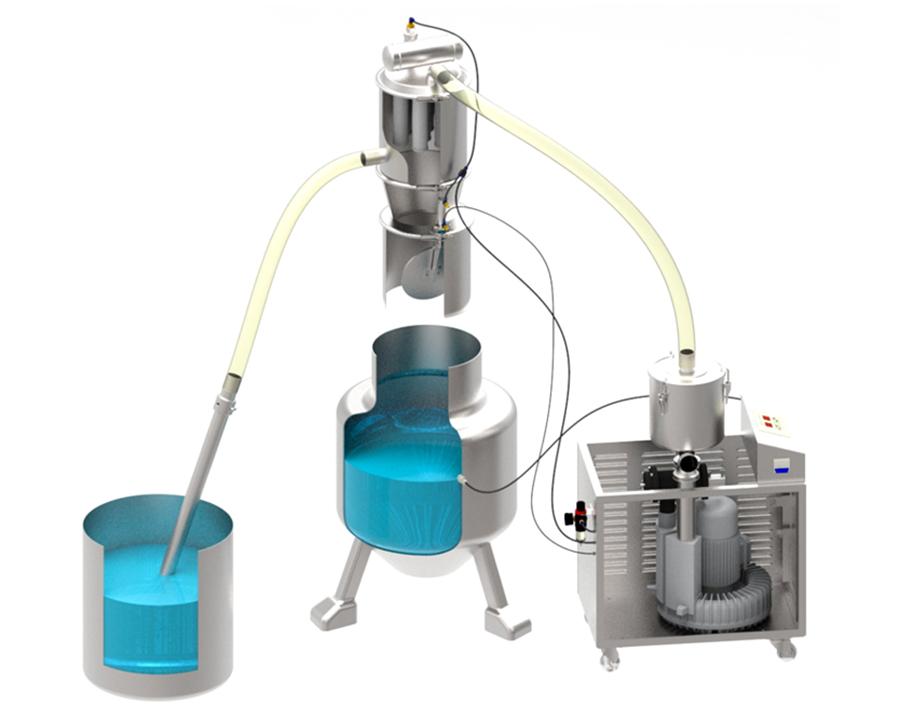

Key Features of Vacuum Feeders
- Mechanism: Negative pressure generated by the vacuum pump moves materials through an enclosed system.
- Material Suitability: Ideal for handling dry and non-sticky materials..
- Hygienic Design: The enclosed design minimizes contamination, making vacuum feeders perfect for pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries.
- Flexibility: Can handle complex layouts, long distances, and height differences efficiently.
Screw Feeder vs. Vacuum Feeder: A Comparative Analysis
| Aspect | Screw Feeder | Vacuum Feeder |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Mechanical rotation of a helical screw blade. | Negative pressure (suction). |
| Material Suitability | Bulk materials | Dry and non-sticky materials. |
| Accuracy | Relatively higher, continuous feeding. | Moderate, depending on vacuum stability. |
| Flexibility | Limited to shorter distances. | Highly flexible; works over long distances. |
| Hygiene | Open systems may lead to contamination. | Enclosed system ensures cleanliness. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning of moving parts. | Easier to clean but dependent on filters. |
Choosing the Right Feeder for Bulk Material Conveying
Choosing between a screw feeder and a vacuum feeder depends on the specific requirements of your application:
- Choose a Screw Feeder if:
- You need high-volume material handling.
- The material is dry, free-flowing and non-cohesive.
- Speed is the top priority.
- Choose a Vacuum Feeder if:
- You handle delicate or non-sticky materials.
- Your application demands an enclosed, contamination-free environment.
- Long-distance or multi-directional conveying is required.
Conclusion
Both screw feeders and vacuum feeders are indispensable in bulk material conveying. Their specific designs cater to unique operational needs, ensuring efficiency, precision, and safety. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each system, you can make an informed decision to optimize your production processes.
For expert advice and high-quality bulk material conveying solutions, contact VTOPS, your trusted partner in industrial automation and packaging technologies.