Single-Phase, Two-Phase, and Three-Phase Electricity: Understanding the Power Needs of Your Packaging Machines in North America
Choosing the right type of power source is crucial for the optimal operation of industrial and commercial equipment, especially for complex and precise devices like packaging machines. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between single-phase, two-phase, and three-phase electricity, and help you understand how to select the appropriate power type for your packaging machine’s specific requirements in North America.
Additionally, we will introduce you to VTOPS, a Chinese top 3 powder packing machine manufacturer that provides many North American customers with a wide range of packaging machines. Their products are praised for their durability and outstanding performance. According to incomplete statistics, VTOPS has provided packaging equipment to North America, especially auger filler and powdered milk filling canning lines, with different degrees of automation for at least 100 home businesses and small and medium-sized enterprises.
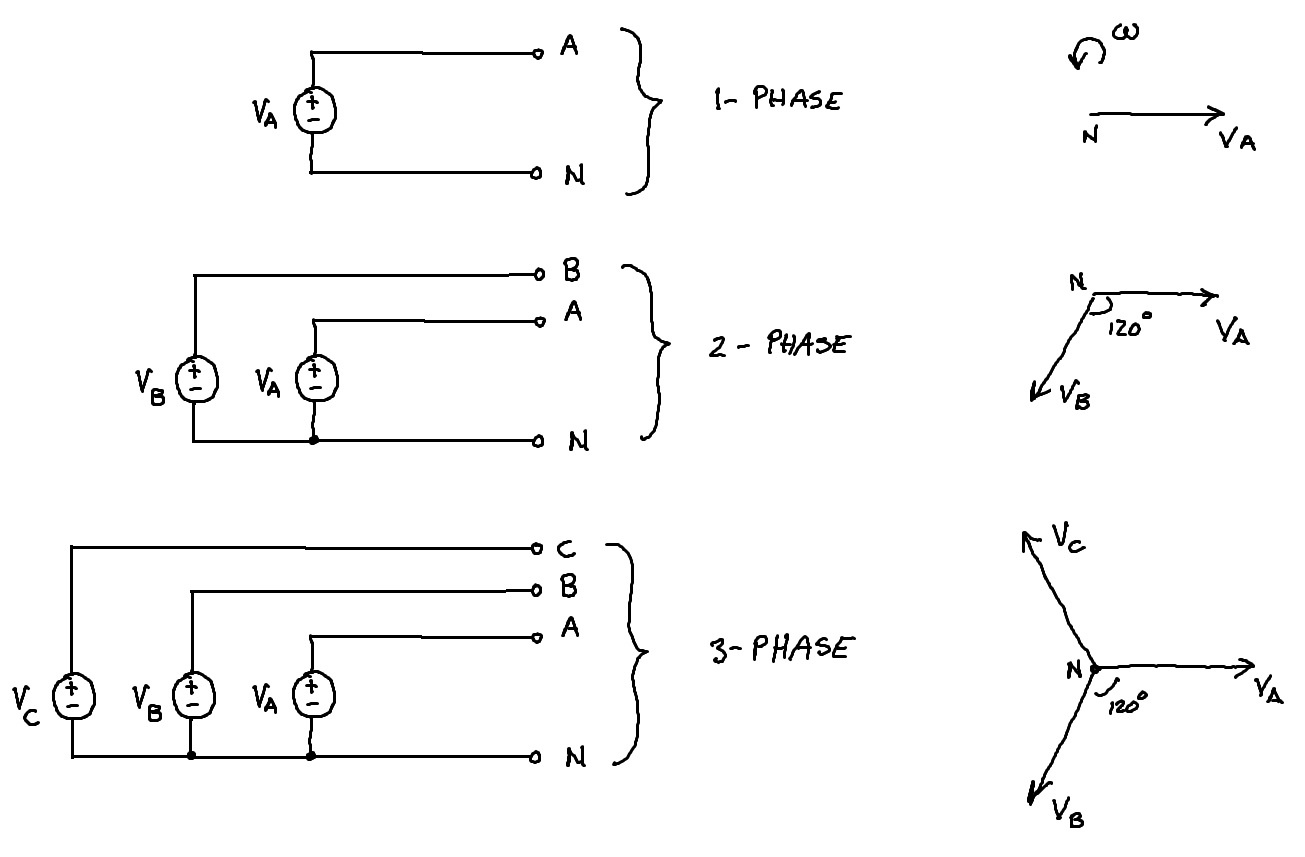
What Is Single-Phase Electricity?
Single-phase electricity is commonly used for households, small businesses, and some small industrial devices like VTOPS’s smaller packaging machines and semi-automatic filling machines. It’s a simple, cost-effective power solution but limited to small loads.
- Standard Voltage in North America: 120/240V
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
What Is Two-Phase Electricity?
Two-phase electricity consists of two alternating currents, each 90 degrees out of phase. Though less common than three-phase, it’s still a suitable choice for many applications. Historically relevant but largely replaced by three-phase electricity due to inefficiencies.
- Standard Voltage in North America: 240V (phase to phase)
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
What Is Two-Phase Electricity?
Three-phase electricity is used for many large industrial devices and commercial facilities. It provides a more stable voltage and is the ideal choice for many high-power demand devices, but at a higher complexity and cost.
Standard Voltage in North America:
- 208 V: Common in Wye connections;
- 240 V: Delta connections in commercial/industrial settings;
- 480 V: Large industrial applications;
- 600 V: Specific heavy industrial applications;
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Installation Considerations
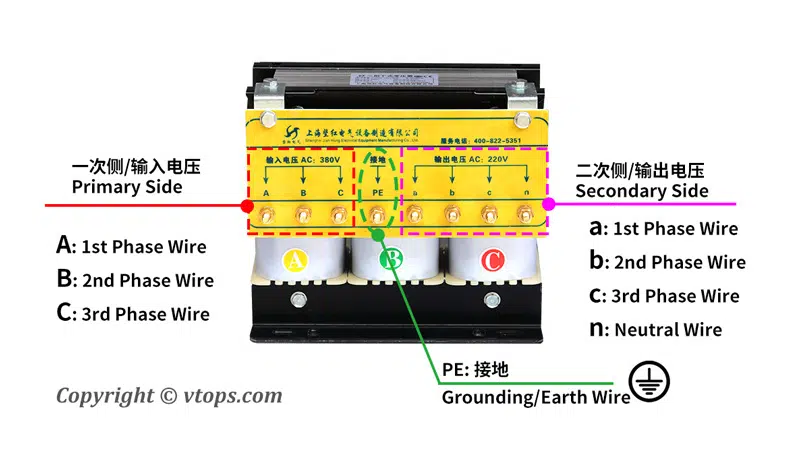
- Ensure Compatibility: Equipment must be compatible with the voltage and frequency of the region. For instance, devices imported from China may require a transformer to adapt to the North American power supply.
- Proper Wiring: The correct specification of wiring must be used, following applicable electrical codes and standards.
- Professional Installation: Qualified electricians should carry out installations to ensure all work complies with local regulations and standards.
- Safe Operation: Follow all safety guidelines and procedures to prevent electrical shocks and other potential hazards.
Compatibility
| Electricity | China | North America |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Phase Electricity | 220V | 120V Compatible by Transformer 240V Compatible |
| Two-Phase Electricity | None | 220V Compatible Required Guidance from Professional Electrician |
| Three-Phase Electricity | 380V | 208V Compatible by Transformer 240V Compatible by Transformer 480V Compatible by Transformer 600V Compatible by Transformer |
Maybe you like further reading: How to Install and Wire An Electrical Voltage Transformer
FAQ
Should I consider frequency as an essential aspect when purchasing a packaging machine in China?
Yes, you should.
The frequency refers to the electrical supply's cycles per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). China's standard frequency is 50 Hz. To ensure that the packaging machinery operates optimally, you should make sure that its frequency rating is compatible with the power supply in the location where it will be used. If there is a discrepancy, you may need to use a converter or transformer to match the frequencies.
In addition, it is worth mentioning that some packaging machines of VTOPS are compatible with the dual standards of 50Hz and 60Hz when designed. This feature allows for greater flexibility without requiring additional converters or transformers. If have any doubts, please consult us to provide the best packaging machine solution.
Single-phase electricity or three-phase electricity, which one is better for packaging machines?
Whether single-phase or three-phase electricity is better depends on the specific application and requirements of the machinery. Here's a general comparison that might guide your decision:
Single-Phase Electricity:
- Simplicity: Often easier to install and maintain.
- Cost: Generally less expensive in terms of installation and equipment.
- Availability: More commonly available in residential areas.
- Usage: Suitable for lighter loads and smaller machinery, like home appliances or small commercial tools.
- Efficiency: Less efficient for heavy machinery; might cause more wear and tear.
Three-Phase Electricity:
- Power: Delivers a continuous and more stable flow of power, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Efficiency: Typically more energy-efficient for industrial equipment, which might save costs in the long run.
- Complexity: Requires more complex wiring and may be more expensive to install.
- Availability: More common in industrial environments, might not be readily available in residential areas.
For Packaging Machines:
- Single-Phase: Suitable for smaller or less demanding packaging operations.
- Three-Phase: Preferred for industrial or heavy-duty packaging tasks that require continuous operation and high efficiency.
In the case of packaging machines, especially for industrial or commercial use, three-phase electricity is often preferable, especially for power over 3 kW. It can provide a smoother operation and is generally more suitable for machines that require consistent and robust power.